|
St. Vincent And The Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines () is an island country in the Caribbean. It is located in the southeast Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, which lie in the West Indies at the southern end of the eastern border of the Caribbean Sea where the latter meets the Atlantic Ocean. Its territory consists of the main island of Saint Vincent and, south of that, two-thirds of the northern part of the Grenadines, a chain of 32 smaller islands. Some of the Grenadines are inhabited— Bequia, Mustique, Union Island, Canouan, Petit Saint Vincent, Palm Island, Mayreau, Young Island—while others are not: Tobago Cays, Baliceaux, Battowia, Quatre, Petite Mustique, Savan and Petit Nevis. Most of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines lies within the Hurricane Alley. To the north of Saint Vincent lies Saint Lucia, to the east is Barbados, and Grenada lies to the south. Saint Vincent and the Grenadines has a population density of over 300 inhabitants/km2 (700 per sq. mi.), with approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus is the Son of God, whose coming as the messiah was prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testament. Christianity began as a Second Temple Judaic sect in the 1st century Hellenistic Judaism in the Roman province of Judea. Jesus' apostles and their followers spread around the Levant, Europe, Anatolia, Mesopotamia, the South Caucasus, Ancient Carthage, Egypt, and Ethiopia, despite significant initial persecution. It soon attracted gentile God-fearers, which led to a departure from Jewish customs, and, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalinago
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated language known as Island Carib. They also spoke a pidgin language associated with the Mainland Caribs. At the time of Spanish contact, the Kalinago were one of the dominant groups in the Caribbean, which owes its name to them. They lived throughout northeastern South America, Trinidad and Tobago, Barbados, the Windward Islands, Dominica, and possibly the southern Leeward Islands. Historically, it was thought their ancestors were mainland peoples who had conquered the islands from their previous inhabitants, the Igneri. However, linguistic and archaeological evidence contradicts the notion of a mass emigration and conquest; the Kalinago language appears not to have been Cariban, but like that of their neighbors, the Taíno. Irving Rouse and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the status of a dependent territory. The commemoration of the independence day of a country or nation celebrates when a country is free from all forms of foreign colonialism; free to build a country or nation without any interference from other nations. Definition of independence Whether the attainment of independence is different from revolution has long been contested, and has often been debated over the question of violence as legitimate means to achieving sovereignty. In general, revolutions aim only to redistribute power with or without an element of emancipation,such as in democratization ''within'' a state, which as such may remain unaltered. For example, the Mexican Revolution (1910) chiefly refers to a multi-factional conflict that e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Assembly Of Saint Vincent And The Grenadines
The House of Assembly of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is the unicameral legislature of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. The House has a total of 23 members: * Fifteen represent single member constituencies and are elected using plurality voting, also known as "first past the post". * Six are known as senators, and are appointed by the Governor-General. Four senators are appointed to represent the government and two to represent the opposition. * One member is the attorney-general, who is appointed * One member is the speaker, who is elected by the government members of the House, in consultation with the Opposition. The most recent elections to the House of Assembly were held on 05 November 2020. The incumbent Unity Labour Party (ULP) was returned to office for an unprecedented fifth consecutive term, winning nine (9) out of fifteen (15) seats. The New Democratic Party (NDP) won the remaining six seats and formed the opposition. See also * List of speakers of the Hou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Gonsalves
Ralph Everard Gonsalves (born 8 August 1946) is a Vincentian politician. He is currently the Prime Minister of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and leader of the Unity Labour Party (ULP).Profile , caribbeanelections.com; accessed 1 September 2014. Gonsalves is the longest continuously serving head of government since St. Vincent and the Grenadines became independent in 1979. He became Prime Minister after his party won a in the 2001 general election. He was the first Prime Minister from the newly constructed ULP, fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susan Dougan
Dame Susan Dilys Dougan ( Ryan; born 3 March 1955) is the Governor-General of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines since 1 August 2019. She is the first woman to hold the office. She was appointed Dame Grand Cross of the Order of St Michael and St George on 29 January 2020 and was appointed an Officer of the Order of the British Empire in the Queen's 2010 Birthday Honour List for services to education and to public administration. Early life and education Susan Dilys Dougan was born in the village of Colonarie in Saint Vincent. She holds a MA (ED) in Curriculum and Evaluation from the University of Southampton, Hampshire, England. Career Dame Susan Dougan began her career as a non-graduate teacher. Over a 34-year career, Dame Susan rose through the ranks of the teaching service to Headmistress of the St. Vincent Girls High School (2001-2004), and later served as Chief Education Officer from 2004 to 2009. She also served as Cabinet Secretary from October 2009 to September ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor-General Of Saint Vincent And The Grenadines
The governor-general of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is the representative of the Vincentian monarch, in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. The office of the governor-general was created in 1979 when the islands gained independence as a Commonwealth realm. List of governors-general of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Following is a list of people who have served as governor-general of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines since independence in 1979. Symbols : Died in office. See also * List of prime ministers of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines * List of colonial governors and administrators of Saint Vincent References World Statesmen {{Representatives of the monarch in Commonwealth realms and Dominions Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Governors-General Government of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Governors-General Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person to accede to the British throne following the death of his mother, Elizabeth II, on 8 September 2022. Charles was born in Buckingham Palace during the reign of his maternal grandfather, King George VI, and was three when his mother ascended the throne in 1952, making him the heir apparent. He was made Prince of Wales in 1958 and his investiture was held in 1969. He was educated at Cheam and Gordonstoun schools, as was his father, Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh. Charles later spent six months at the Timbertop campus of Geelong Grammar School in Victoria, Australia. After earning a Bachelor of Arts degree from the University of Cambridge, Charles served in the Air Force and Navy from 1971 to 1976. In 1981, he married Lady Diana Spencer, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchy Of Saint Vincent And The Grenadines
The monarchy of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is the constitutional system of government in which a hereditary monarch is the sovereign and head of state of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, forming the core of the country's Westminster-style parliamentary democracy. The Crown is thus is the foundation of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches of the Vincentian government. While Royal Assent and the royal sign-manual are required to enact laws, letters patent, and orders in council, the authority for these acts stems from the Vincentian populace, and, within the conventional stipulations of constitutional monarchy, the sovereign's direct participation in any of these areas of governance is limited, with most related powers entrusted for exercise by the elected and appointed parliamentarians, the ministers of the Crown generally drawn from amongst them, and the judges and Justices of the Peace. The Vincentian monarchy has its roots in the French and British cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies differ from absolute monarchies (in which a monarch is the only decision-maker) in that they are bound to exercise powers and authorities within limits prescribed by an established legal framework. Constitutional monarchies range from countries such as Liechtenstein, Monaco, Morocco, Jordan, Kuwait, and Bahrain, where the constitution grants substantial discretionary powers to the sovereign, to countries such as Australia, the United Kingdom, Canada, the Netherlands, Spain, Belgium, Sweden, Malaysia, Thailand, Cambodia, and Japan, where the monarch retains significantly less personal discretion in the exercise of their authority. ''Constitutional monarchy'' may refer to a system in which the monarch acts as a non-party political head of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliamentary System
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of the legislature, typically a parliament, to which it is accountable. In a parliamentary system, the head of state is usually a person distinct from the head of government. This is in contrast to a presidential system, where the head of state often is also the head of government and, most importantly, where the executive does not derive its democratic legitimacy from the legislature. Countries with parliamentary systems may be constitutional monarchies, where a monarch is the head of state while the head of government is almost always a member of parliament, or parliamentary republics, where a mostly ceremonial president is the head of state while the head of government is regularly from the legislature. In a few parliamentary republics, among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
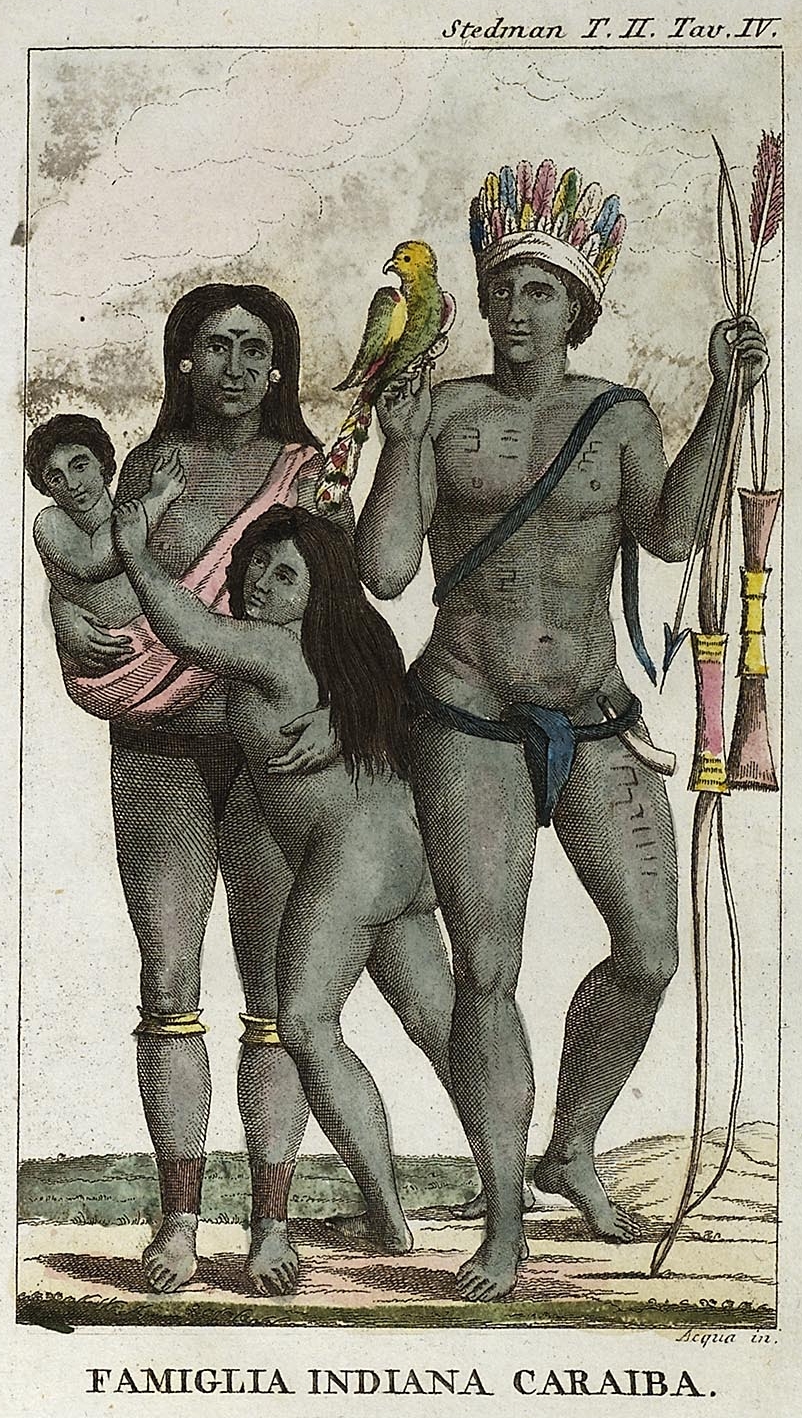
%2C_by_John_Trumbull.jpg)




